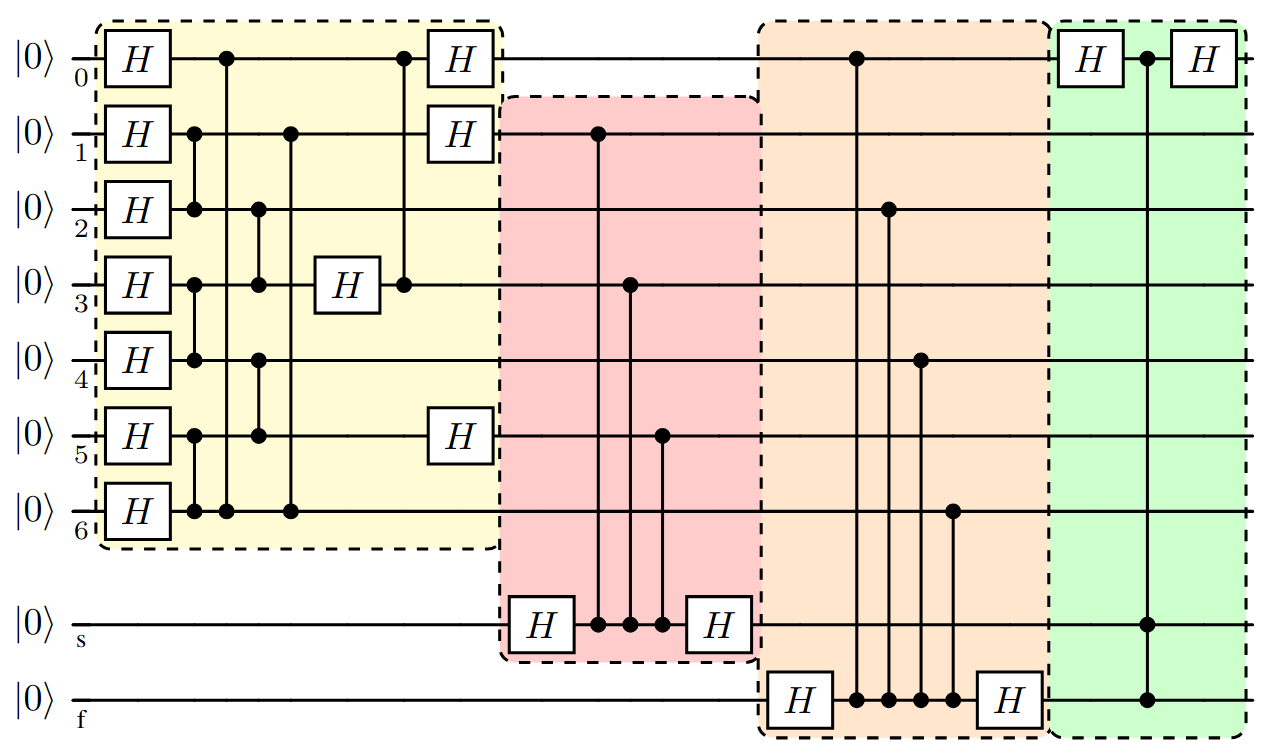
THE QUANTUM LÄND
Rydberg Quantum Computers & Simulators made in Stuttgart.
About
In the very south-west corner of Germany, we work towards realizing fully functional quantum computers and quantum simulators made in THE LÄND Baden-Württemberg. Our research laboratories can be found at the 5th Institute of Physics (University of Stuttgart). We can built on more than 15 years of fundamental research on Rydberg atoms, to now turn powerful scientific concepts into real-world applications.
Visit our projects, to learn how we aim to realize a quantum computer demonstrator with hundreds of qubits, study novel qubits concepts for quantum simulation, or develop key technology needed to improve the performance of our machines.

Our quantum machines are built at the
University of Stuttgart
Baden-Württemberg (Germany)
Technology
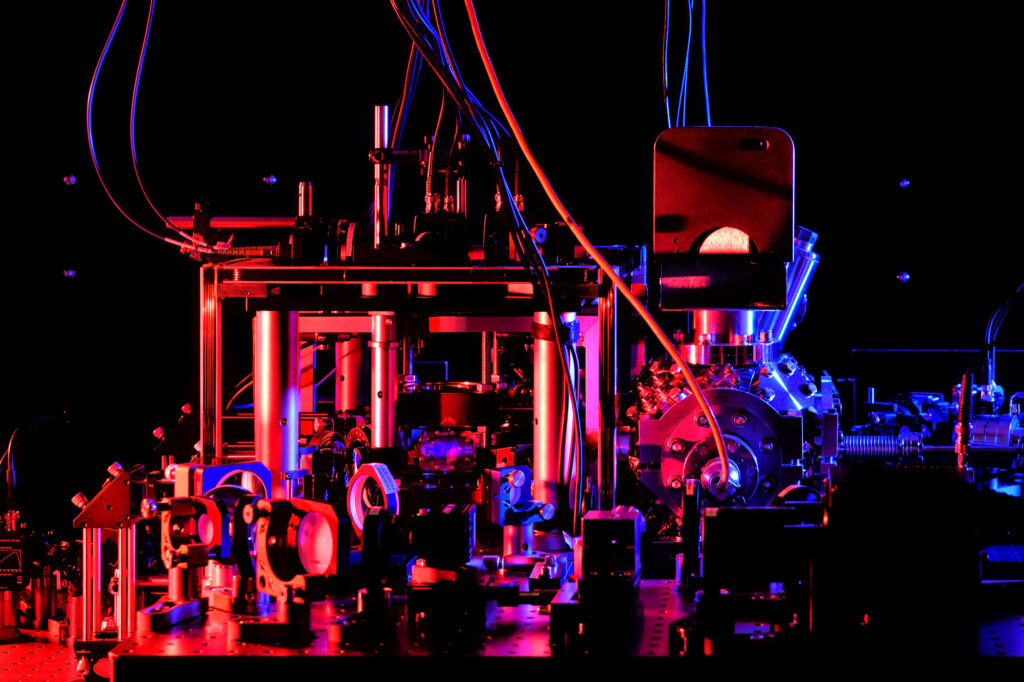
Our machines utilize individually controlled Strontium atoms as qubits. To this end, we employ laser-cooling to chill our atoms down to temperatures just a millionth of a degree above absolute zero. Under these almost ideal conditions, the atoms can be arranged in versatile and scalable qubit arrays using optical tweezers. Exciting the atoms to Rydberg states with lasers, allows us to let them interact in a highly controlled way, which is key to perform high-fidelity quantum computations and simulations.
Latest News
-
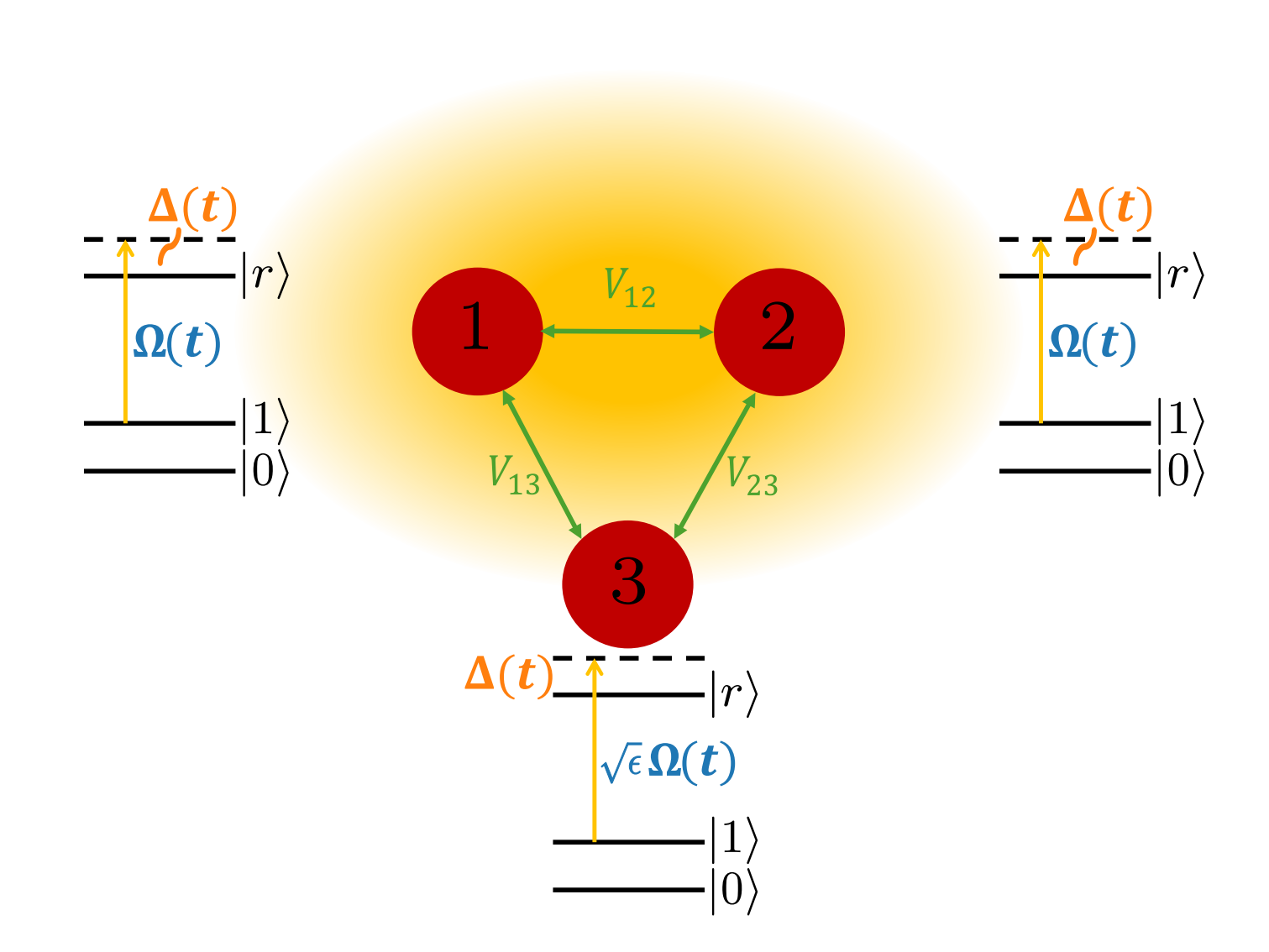
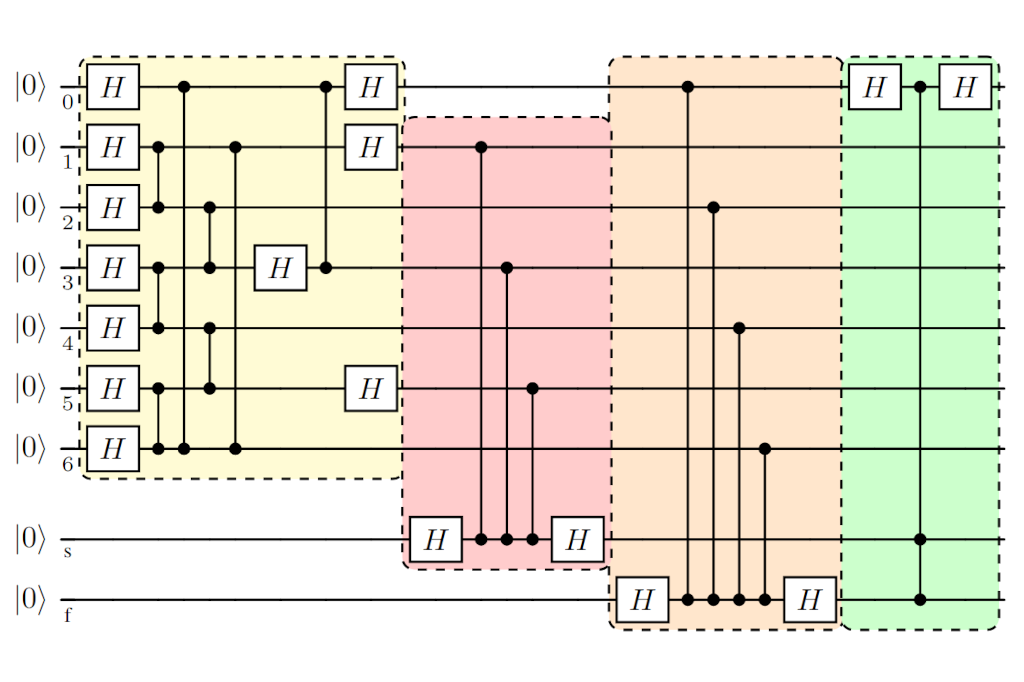
Suppressing crosstalk for Rydberg quantum gates
In our new publication, we develop a method to suppress crosstalk from implementing controlled-Z gates via local addressing in neutral atom quantum computers.
-
Project for benchmarking Rydberg quantum computers launched
We are very happy to announce that our benchmarking consortium BeRyQC is now funded by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research.
-
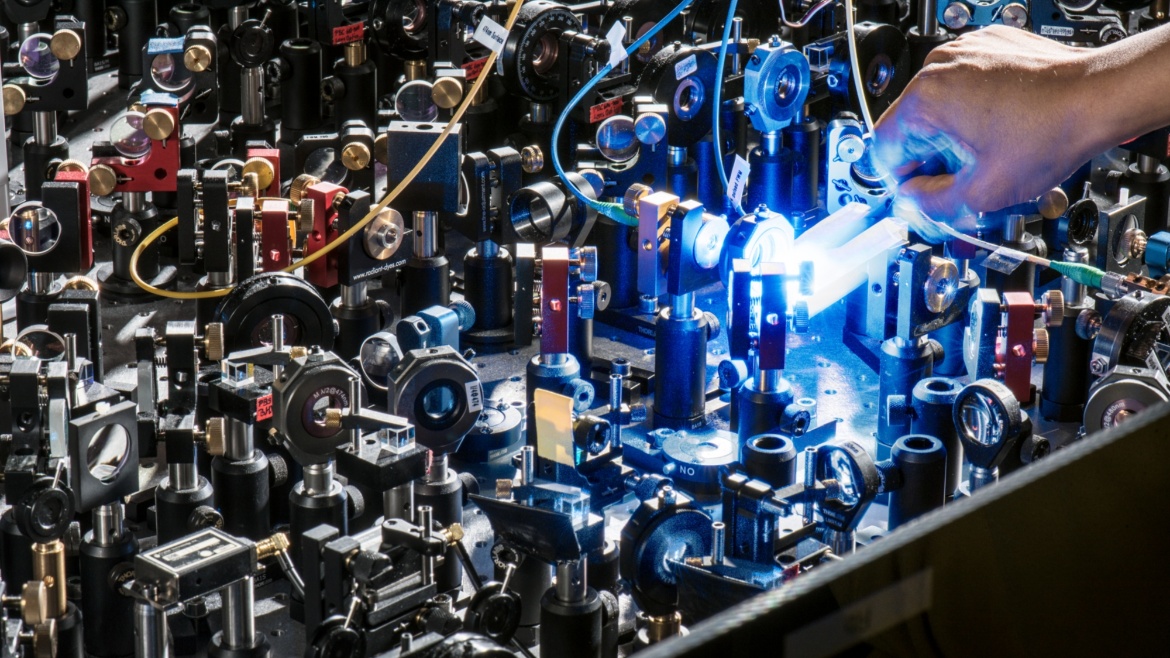
Join our ATOMIQ webinar on May 8th
We are excited to invite you to a webinar that showcases our unified, modular quantum hardware orchestration platform atomiq on March 8th, 10am (CEST) …
Projects
You want to join us?